A Novel Gel Electrophoresis Technique for Rapid Biomarker Diagnosis via Mass Spectrometry
Development of a rapid recovery method of target protein biomarkers using dissolvable polyacrylamide gel and its application to mass spectrometry
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis enables high-resolution separation of proteins extracted from biological samples, but it requires more than one day of pretreatment to recover the separated proteins trapped inside the gel for detection by mass spectrometry. BAC-DROP, our novel electrophoresis technology, uses a dissolvable form of polyacrylamide gel, which allows sample pretreatment to be completed in about 5 hours. The developed technology will enable the rapid diagnosis of viruses and disease protein markers.
Mass spectrometry (MS) is a powerful method for biomarker analysis because it enables highly sensitive and accurate measurement of target molecules in clinical samples. The application of MS to clinical diagnosis, such as neonatal metabolic screening, has been progressing with a focus on metabolite markers. MS measurement of proteins is currently mainly used for novel marker discovery studies, but there is a growing interest in its application in clinical marker diagnosis as an alternative to immunoassays.
MS-based quantification of protein biomarkers is mainly performed by a bottom-up approach using peptide fragments obtained by enzymatic protein digestion with trypsin. Standard digestion protocols require a reaction time of more than 20 hours, which is a rate-limiting factor in sample preparation workflows.
Although protein quantification by MS is highly sensitive, plasma and serum proteome are highly complex, and interference by other components poses a significant challenge. For high-precision detection of target markers, approaches for pre-removal of major serum protein components such as albumin or selective enrichment of target markers using antibody columns have been reported, but the off-target effect on quantitative results and the difficulty of processing multiple samples remain obstacles.
In this study, we focused on dissolvable polyacrylamide gels using N,N’-Bis(acryloyl)cystamine (BAC) as a cross-linker to solve these problems. BAC cross-linked polyacrylamide gels readily dissolve by reduction treatment, allowing the recovery of proteins that have escaped into the solution. We found that the recovered proteins were suitable for rapid trypsin digestion under high temperature conditions, and we succeeded in establishing a high-throughput sample preparation method for MS-based biomarker quantification, which we named BAC-DROP (BAC-Gel Dissolution to Digest PAGE-Resolved Objective Proteins).
High-resolution proteome fractionation with BAC-DROP is particularly effective for MS quantification of targeted trace marker proteins derived from clinical samples. By introducing BAC-DROP into the MS-based quantification workflow of the inflammatory biomarker C-reactive protein (CRP), we were able to complete the sample pretreatment in only 5 hours and successfully quantified CRP from a 0.5 µL human serum sample. We also succeeded in a serological diagnosis of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection by HBsAg quantification combined with BAC-DROP and MS. Recently, interest in MS diagnosis of viral infections has been rapidly increasing, as exemplified by the diagnosis of COVID-19. The high-throughput sample preparation approach by BAC-DROP shown in this study will be applicable not only to HBV but also to other infectious viral disease samples.
This research was conducted by a collaborative research group of Ehime University, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, and Kitasato University, and the research results were published online in the Journal of Proteome Research of the American Chemical Society on December 24, 2020.
Reference URL: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00749
Bibliographic Information
BAC-DROP: Rapid Digestion of Proteome Fractionated via Dissolvable Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis and Its Application to Bottom-Up Proteomics Workflow.
Takemori A, Ishizaki J, Nakashima K, Shibata T, Kato H, Kodera Y, Suzuki T, Hasegawa H, Takemori N.
J Proteome Res. 2020 Dec 24. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00749.
Fundings
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 16K08937
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 17K19926
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 17H02206
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 19K05526
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 20H04713
- AMED JP17ek0109104
- AMED JP20ek0109360
- AMED JP19fk0310102
- AMED JP19fk0310103
- AMED JP19bk0104090h0001
Media
-
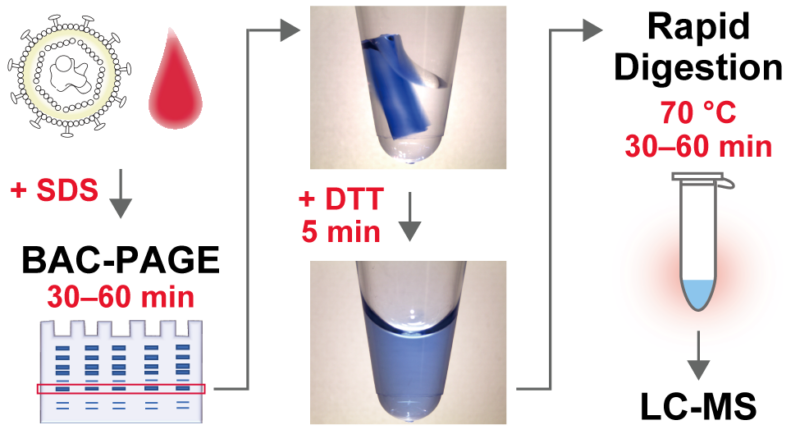
High-throughput sample preparation for mass spectrometry-based protein analysis using BAC-DROP
Dissolvable BAC cross-linked gels allow rapid and lossless recovery of protein biomarkers separated by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and facilitate analysis by mass spectrometry
credit : Reprinted with permission from Journal of Proteome Research © 2020 American Chemical Society (ACS)
Usage Restriction : Please get copyright permission
Contact Person
Name : Nobuaki Takemori
Phone : +81-89-960-5499
E-mail : takemori@m.ehime-u.ac.jp
Affiliation : Advanced Research Support Center
