A Stress Memory Effect in Olivine at Upper Mantle Pressures and Temperatures
The Kaiser effect, which is known as a stress memory effect, predicts that seismic events occur only when the previous maximum stress is exceeded. However, the Kaiser effect has only been tested at room temperature in laboratories. Here, we performed deformation experiments on natural olivine at high pressures and high temperatures. We have successfully confirmed a stress memory effect in strongly deformed olivine at high pressures and high temperatures.
The Kaiser effect, which is known as a stress memory effect, predicts that seismic events occur only when the previous maximum stress is exceeded. Therefore, the Kaiser effect has been applied for the estimation of the magnitude of ‘in situ’ stress on crustal rocks in the community of geotechnical engineering (including forecasting earthquakes). Geodetic observations have revealed that the time dependency of seismicity synchronized with inflation/deflation of a volcano is well explained by the Kaiser effect. However, the Kaiser effect has only been tested at room temperature in laboratories. Here, we performed deformation experiments on natural olivine at high pressures and high temperatures via a state-of-the-art technology large-volume deformation apparatus combined with a microseismicity monitoring technique. We have successfully confirmed a stress memory effect (corresponding to the Kaiser effect in a broad meaning) in strongly deformed olivine at high pressures and high temperatures. The observed memory effect could be effective in the seismic zones of subducting slabs.
Reference URL: https://doi.org/10.1029/2025GL114960
Bibliographic Information
A Stress Memory Effect in Olivine at Upper Mantle Pressures and Temperatures
Tomohiro Ohuchi, Yuji Higo, Noriyoshi Tsujino, Sho Kakizawa, Yusuke Seto, Yoshio Kono, Hirokatsu Yumoto, Takahisa Koyama, Hiroshi Yamazaki, Yasunori Senba, Haruhiko Ohashi, Ichiro Inoue, Hiroyuki Ohsumi, Yujiro Hayashi, Makina Yabashi, and Tetsuo Irifune
Geophysical Research Letters, 52, e2025GL114960,
doi:10.1029/2025GL114960
Fundings
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 19H00722,23H00147
- Mitsubishi foundation 202310008
Media
-
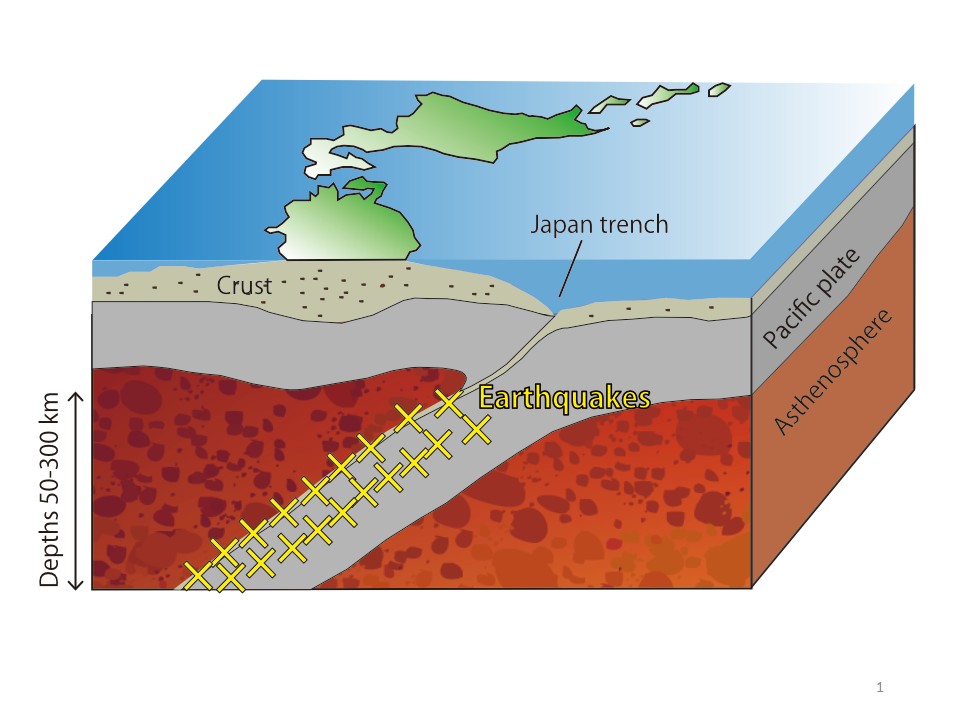
【Fig.1】Subducting slab and intermediate earthquakes underneath Honshu island
Intermediate earthquakes occur in the subducting slabs at depths of 50-300 km. Hypocenters of intermediate earthquakes form seismic zones.
credit : Tomohiro Ohuchi
Usage Restriction : Please get copyright permission -
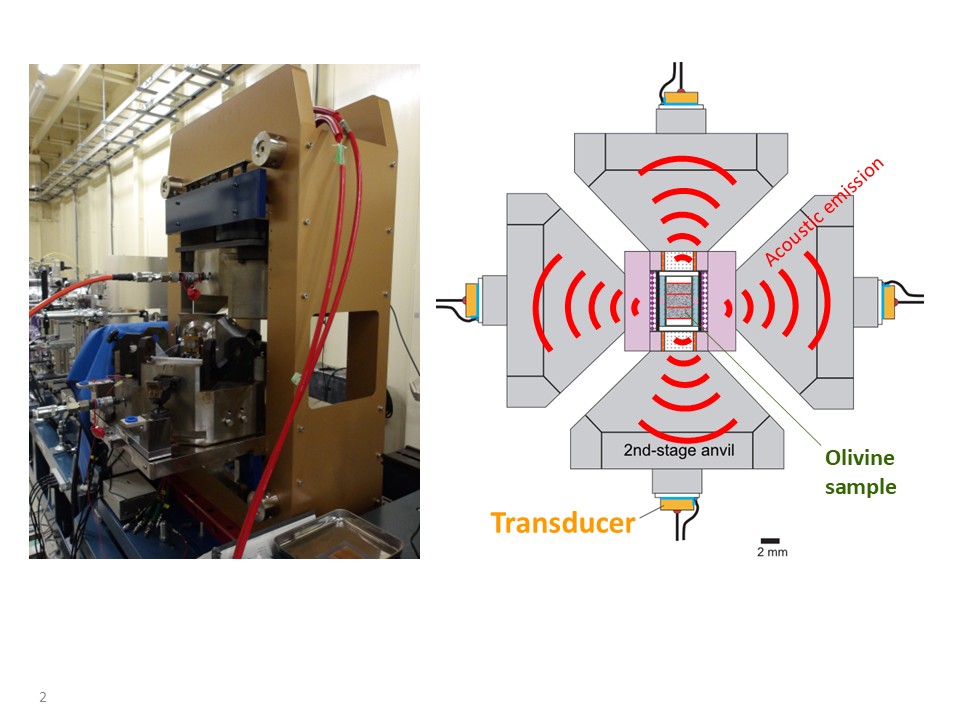
【Fig.2】Multianvil apparatus (left) and monitoring of acoustic emissions at high pressures and high temperatures (right)
A cubic pressure medium (pink) is surrounded by six anvils. Transducers, which are used for the detection of P-waves, are pasted on the rear side of each anvil.
credit : Tomohiro Ohuchi
Usage Restriction : Please get copyright permission -
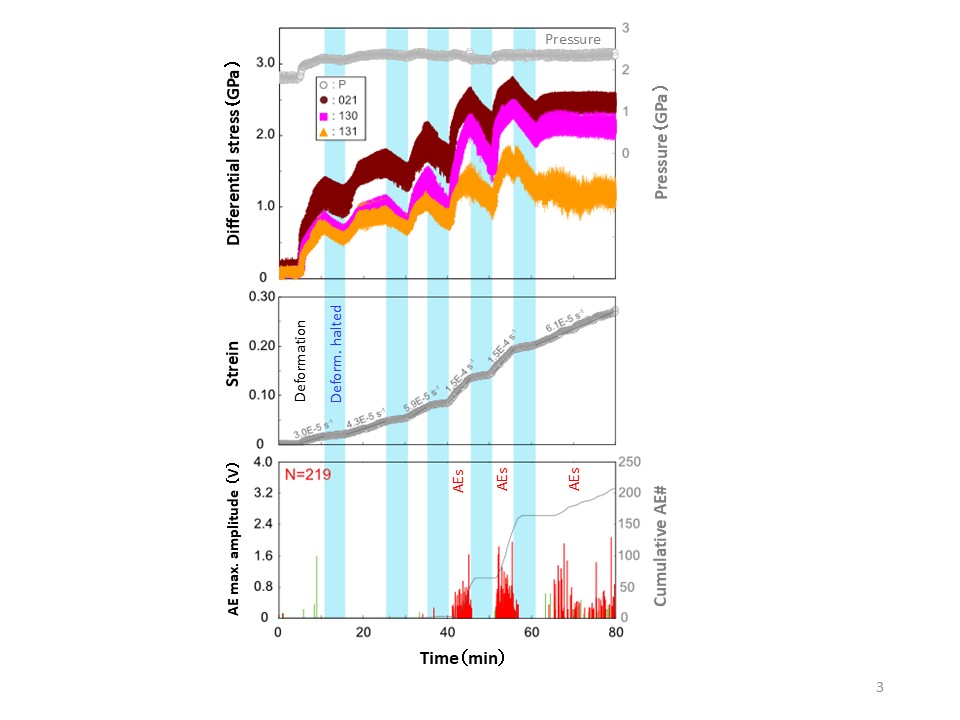
【Fig.3】Cyclic deformation experiments on olivine samples at pressures of ~2.3 GPa and a temperature of 880 deg.C
Differential stress and strain increased during the deformation periods (white areas). Differential stress decreased when the deformation was halted (stress-relaxation periods: blue areas). Radiation of acoustic emissions (AEs) occurred during the deformation periods, though AEs ceased during the stress-relaxation periods. These results show the manifestation of the Kaiser effect. However, radiation of AEs proceeded at higher strains (> 0.2) even though the differential stress was below the maximum value (i.e., breakdown of the Kaiser effect).
credit : Tomohiro Ohuchi
Usage Restriction : Please get copyright permission
Contact Person
Name : Tomohiro Ohuchi
Phone : +81-89-927-8159
E-mail : ohuchi.tomohiro.mc@ehime-u.ac.jp
Affiliation : Geodynamics Research Center, Ehime University


