The important role of seemingly “lazy” electrons residing in magnetic materials
Quantum criticality induced by “lazy” valence electrons
Valence electrons exhibit electrical conductivity and magnetism. Initially, we studied magnetic spin ordering in triangular lattice semiconductors using light. However, about half of these electrons did not directly contribute to magnetism. Instead, two such electrons formed weakly bound pairs, similar to superconductors. Considering all valence electrons, the system resembles a quantum spin liquid. Our findings show that these previously overlooked "inactive" electrons play a vital role in quantum properties.
[Introduction]
Molecular crystals with conductivity and magnetism, due to their low impurity concentrations, provide valuable insights into valence electrons. They have helped link charge ordering to superconductivity and to explore quantum spin liquids, where electron spins remain disordered even at extremely low temperatures. Valence electrons with quantum properties are also expected to exhibit emergent phenomena, making these crystals essential for studying novel material functionalities.
However, the extent to which valence electrons in molecular crystals contribute to magnetism remains unclear, leaving their quantum properties insufficiently explored. To address this, our research team used light to analyze valence electron arrangements, building on studies of superconductors and quantum spin liquids.
[Methods]
The molecular crystal (C₂H₅)(CH₃)₃As[Pd(C₃S₅)₂]₂ contains [Pd(C₃S₅)₂]₂ molecules at the vertices of a triangular lattice, with one valence electron “formally” assigned to each vertex. The actual distribution of these electrons was experimentally determined. Synchrotron infrared light, along with near-infrared and visible laser light, was used to irradiate the crystal, inducing molecular vibrations. Analyzing the vibrational frequencies revealed details about valence electron locations, mobility ranges, and whether inter-molecular distances were constant or variable. This enabled the study of valence electron arrangements within the crystal.
[Results]
Initially believed to be magnetic, the material was discovered to have about half of its valence electrons not contributing to magnetism, instead forming pairs. These pairs exhibited properties reminiscent of a superconducting state driven by charge fluctuations. As the temperature decreased, the number of pairs increased and eventually saturated, while the remaining electrons formed an antiferromagnetic arrangement. At extremely low temperatures, electrons contributing to magnetism coexisted with non-magnetic electrons, forming a fixed arrangement on the triangular lattice. This mixed state closely resembles a frozen configuration of dynamic valence electrons observed in spin-liquid candidate materials.
[Implications]
This study reveals the hidden potential of valence electrons that do not contribute to magnetism in uncovering properties relevant to superconductivity, magnetic resistance, and spintronics. Furthermore, it bridges the gap between non-magnetic and magnetism-related superconductors, paving the way for future research into quantum material properties.
Reference URL: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.110.205126
Bibliographic Information
Charge and valence bond orders in the spin-1/2 triangular antiferromagnet
Takashi Yamamoto, Takashi Fujimoto, Yasuhiro Nakazawa, Masafumi Tamura, Mikio Uruichi, Yuka Ikemoto, Taro Moriwaki, HengBo Cui, and Reizo Kato
Phys. Rev. B 110, 205126 – Published 12 November, 2024
Fundings
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant Number 15K05478, 19K05405, 16H06346, and 23K04691
Media
-
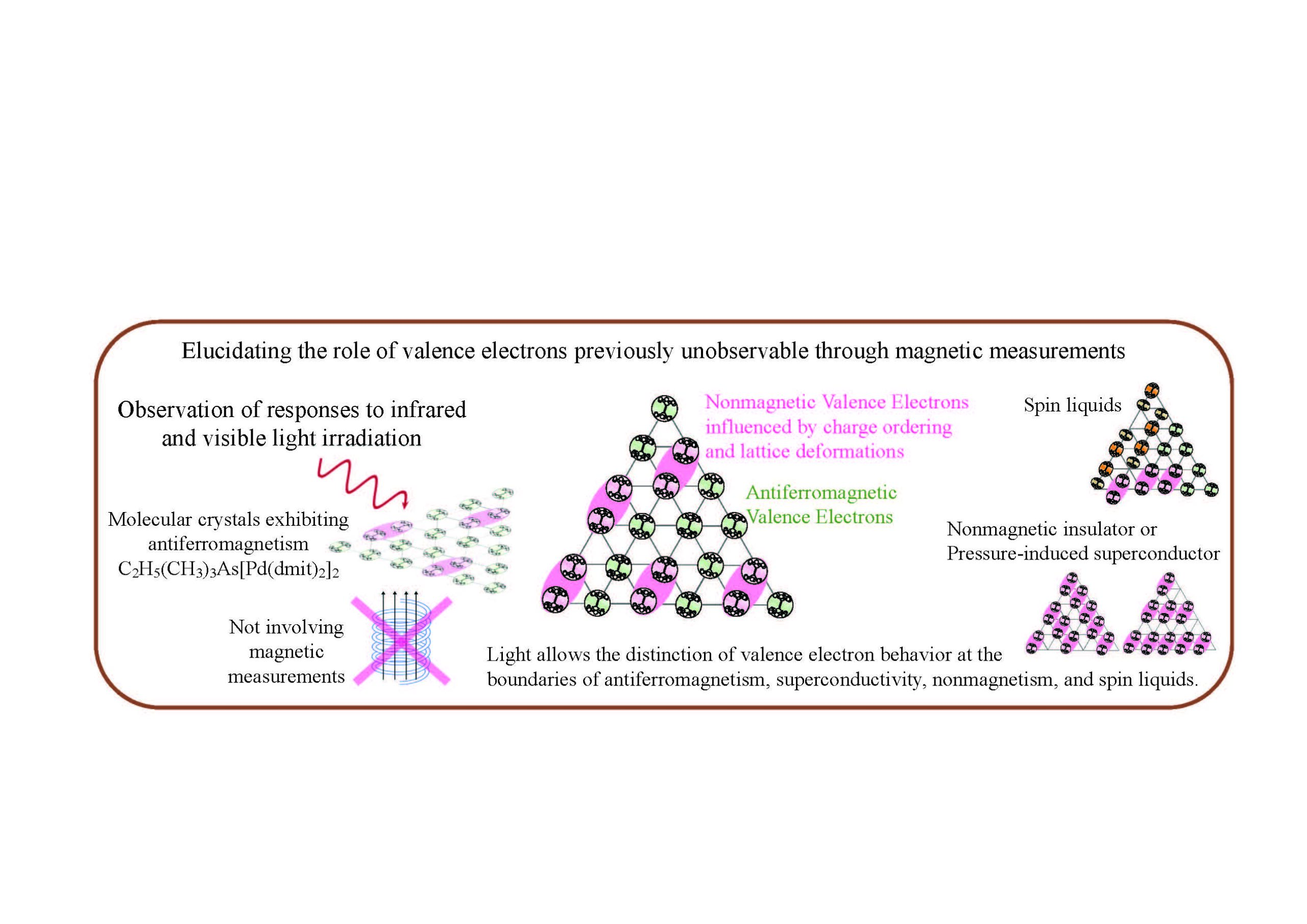
Distribution of Valence Electrons in Antiferromagnetic Molecular Crystals with a Triangular Lattice
Using synchrotron infrared light and near-infrared/visible lasers without applying a magnetic field, we observed the response of valence electrons in the (C₂H₅)(CH₃)₃As[Pd(C₃S₅)₂]₂ crystal. The results revealed that approximately half of the valence electrons contribute to antiferromagnetism, while the other half form weak pairs associated with charge ordering and lattice distortion. By comparing the valence electron arrangement identified in this study with previously reported spin liquids and superconductors, significant similarities were discovered.
credit : Takashi Yamamoto, Ehime University
Usage Restriction : Please get copyright permission
Contact Person
Name : Takashi Yamamoto
Phone : +81-89-927-9608
E-mail : yamataka@ehime-u.ac.jp
Affiliation : Graduate School of Science and Engineering, Ehime University
